Multi-Frequency Current Injection for Low or Highly Variable Zero-Sequence Voltages
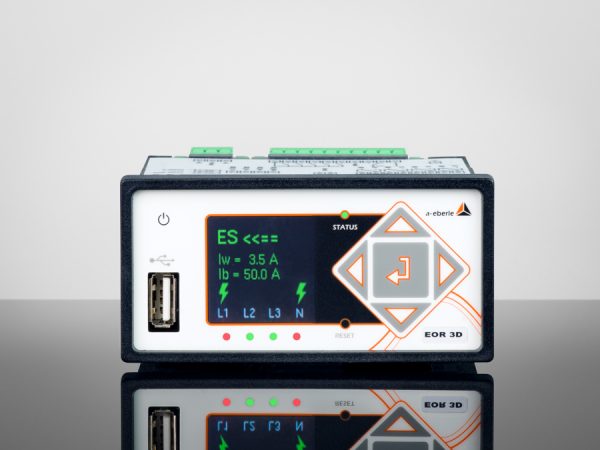
MCI
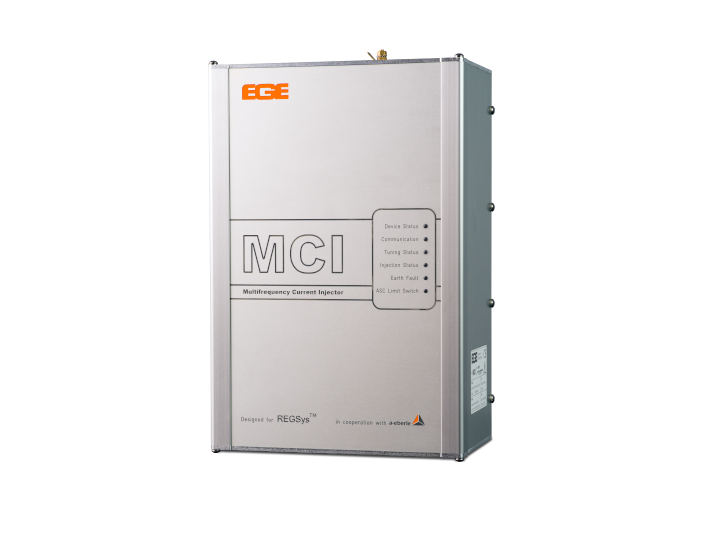
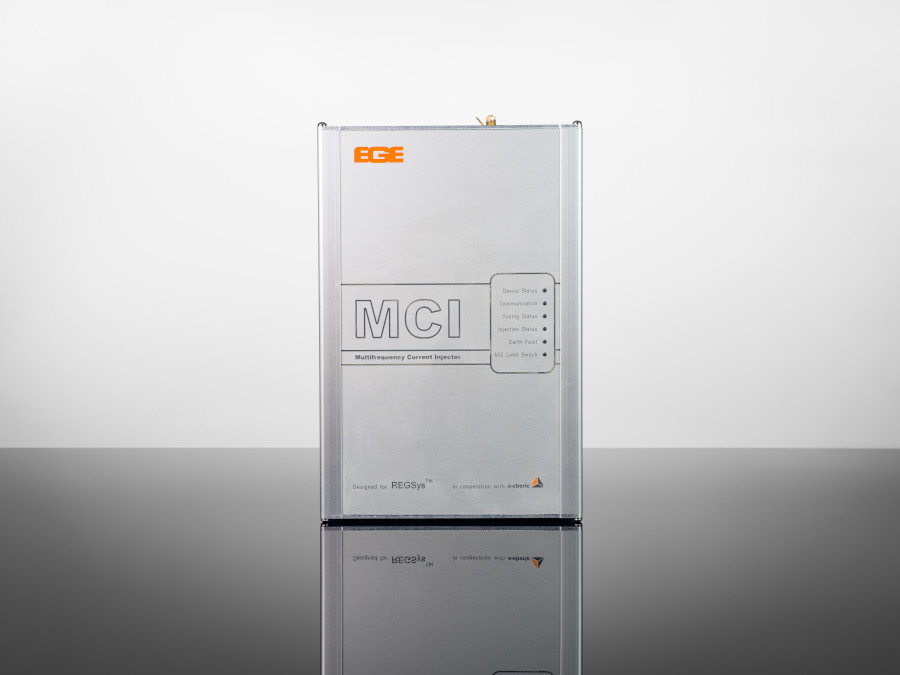










Multi-frequency current injection
MCI
The classic regulation process, i.e. searching for the resonance curve across the range of travel of the coil, can no longer successfully adjust the arc suppression coil in certain network situations. We have developed this multi-frequency current injection for the increasingly frequent cases where the zero-sequence voltage is highly disturbed or subject to extreme influences or where networks are highly symmetrical. The current injection creates a signal that is fed into the network via the auxiliary power winding of the arc suppression coil. From the network reaction, the combined REG-DP(A) and current injection are able to calculate a resonance curve despite the low or highly variable zero-sequence voltage.
Further questions or want to start an enquiry? Please click “Product Enquiry”.

Cross-product downloads

Cross-product downloads
Special Publications
Product overview A. Eberle

MCI

MCI
Technical Data Sheets
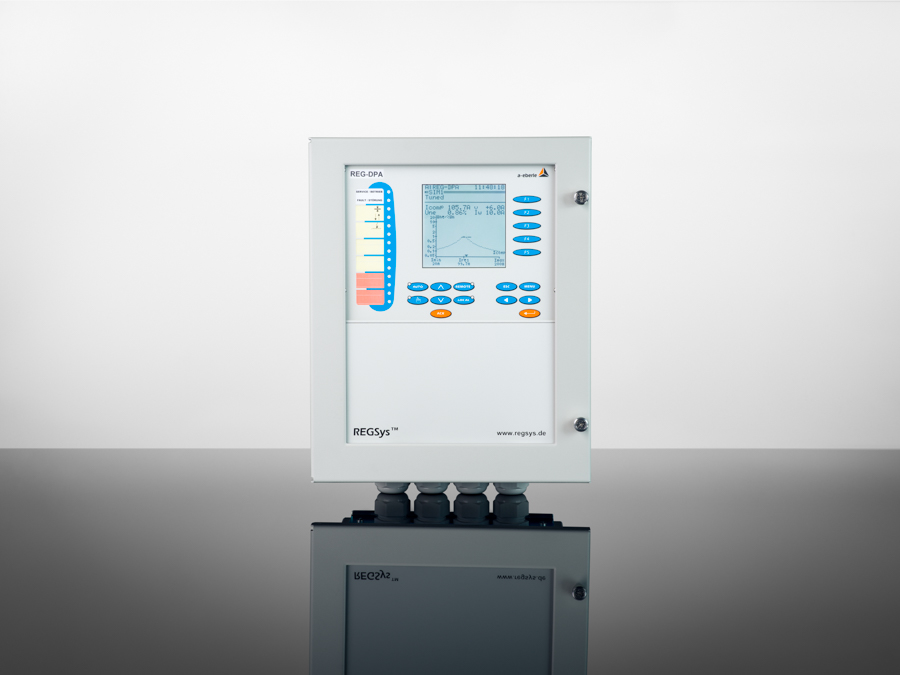
Instruction Manual REG-DP(A)
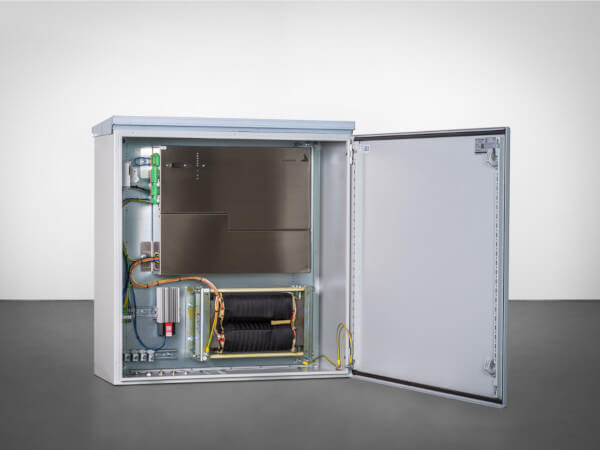
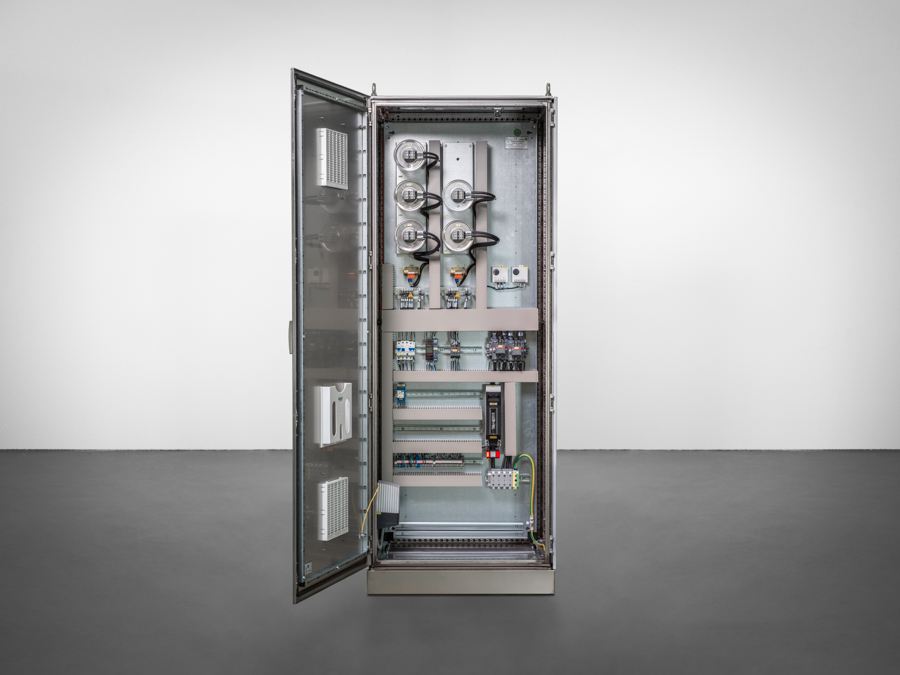
Compact dimensions, no inductors and no additional voltage transformer necessary
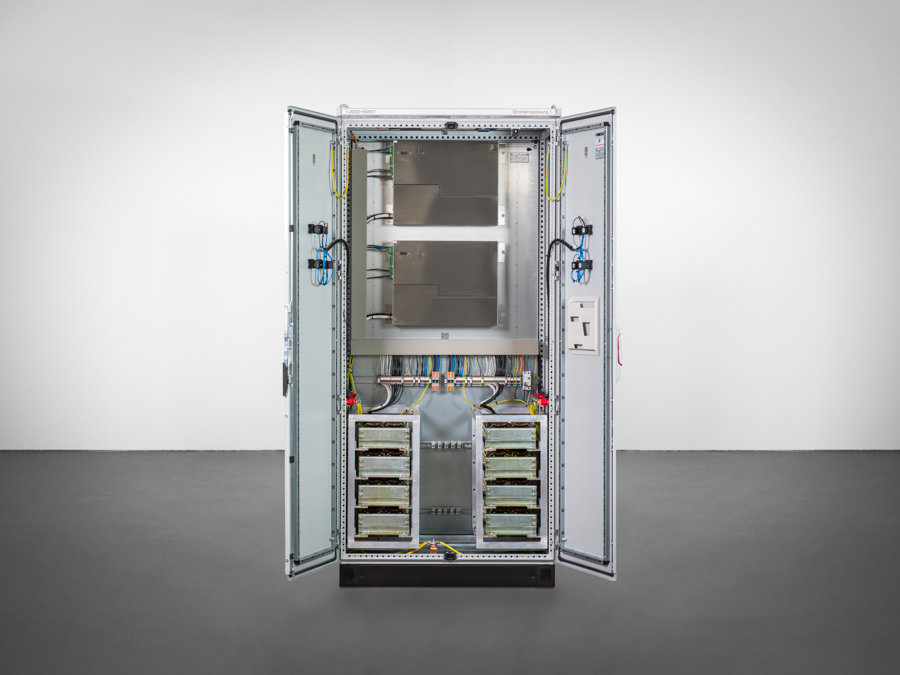
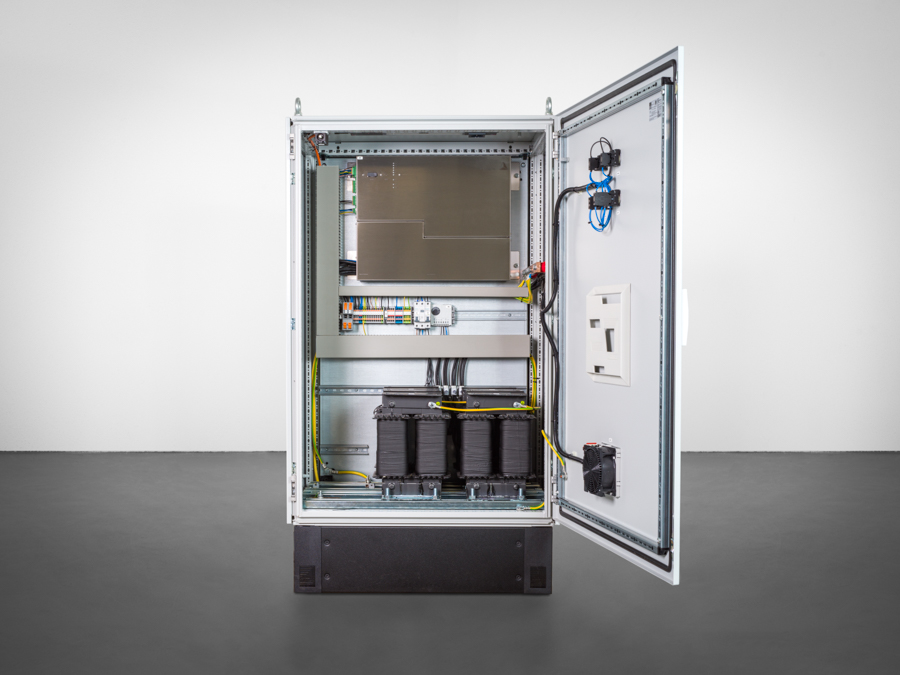
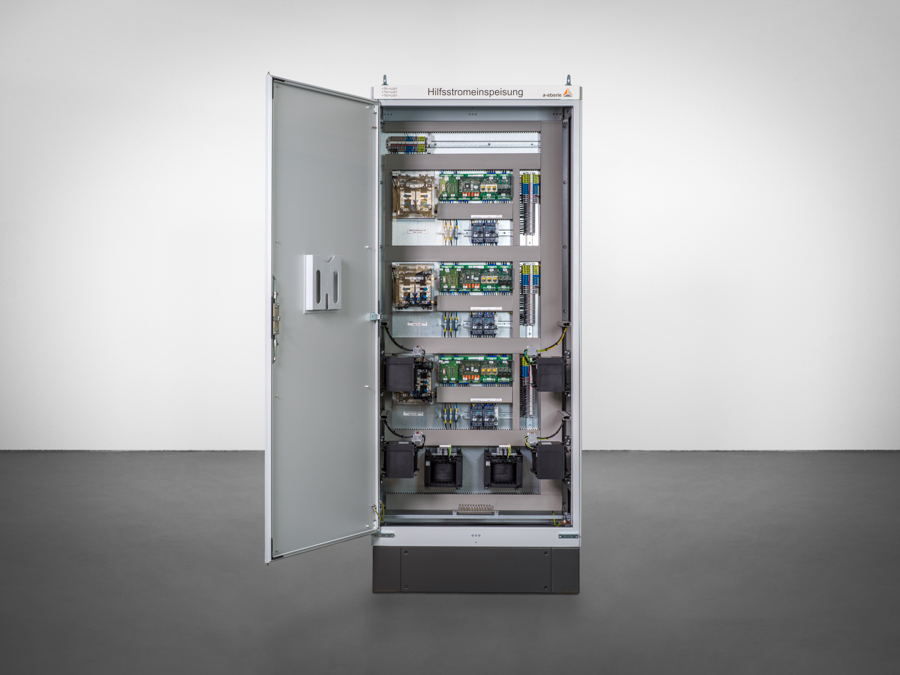
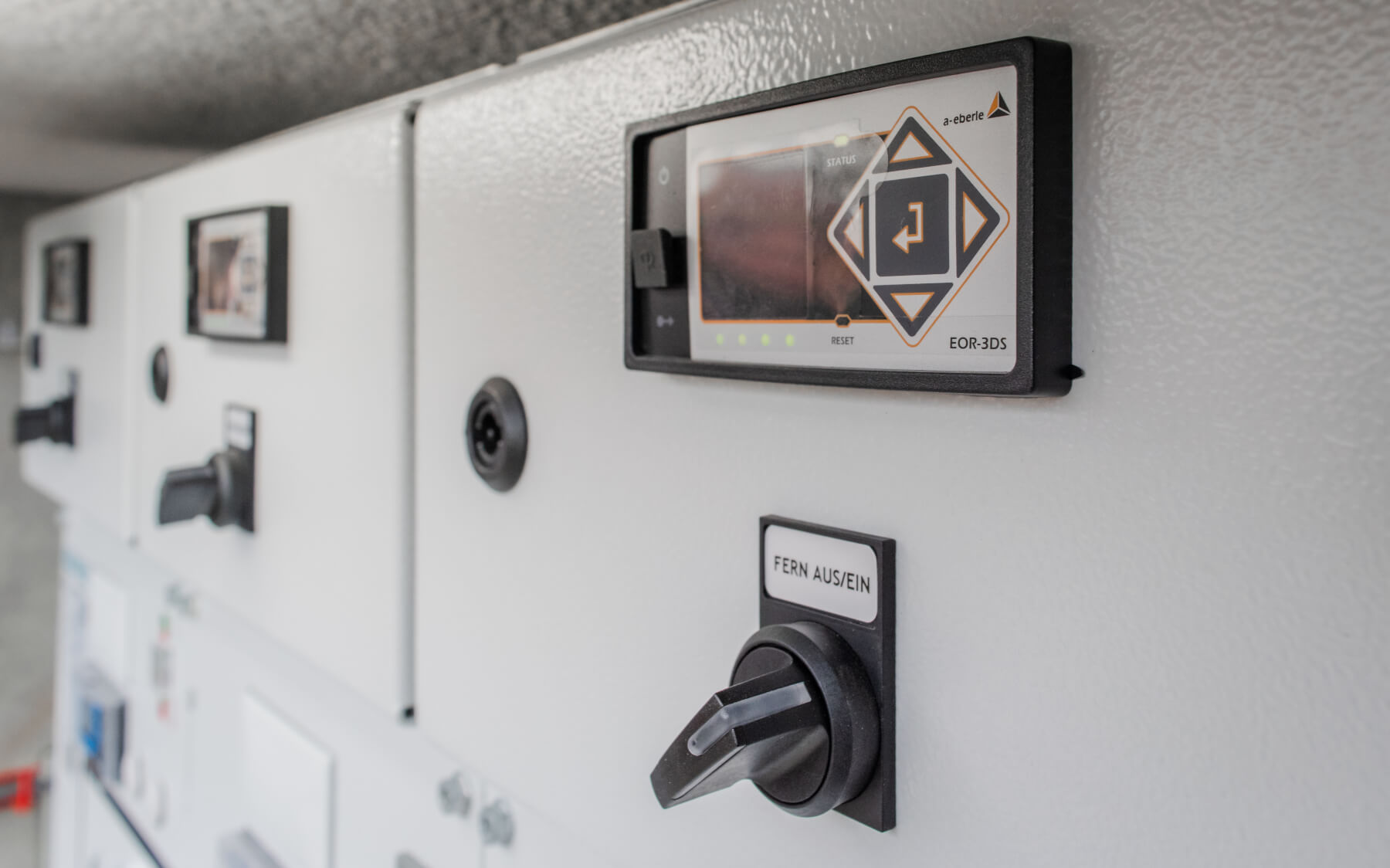
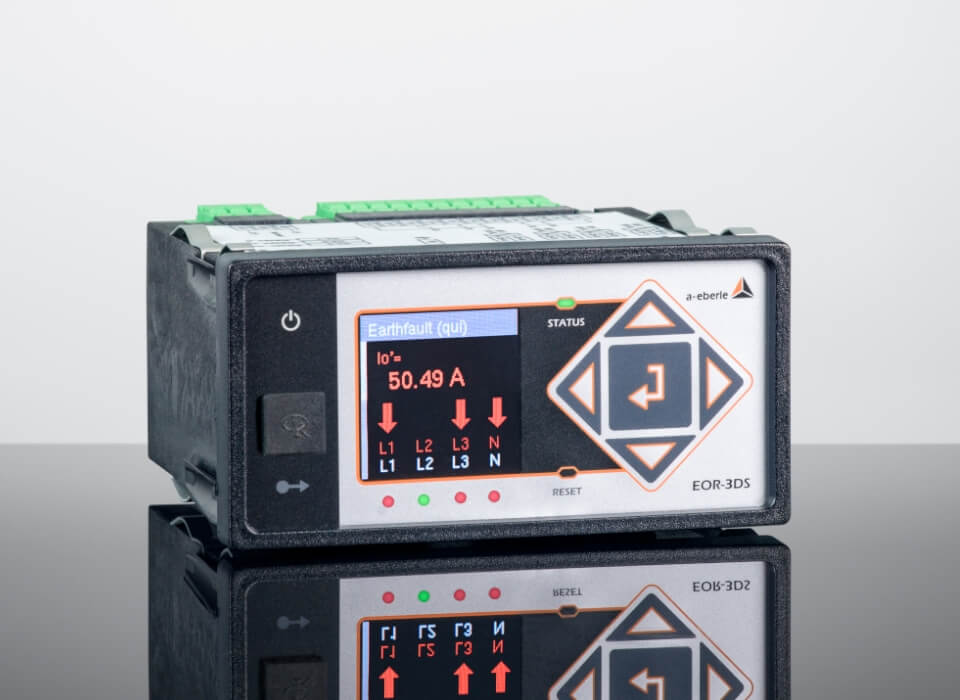
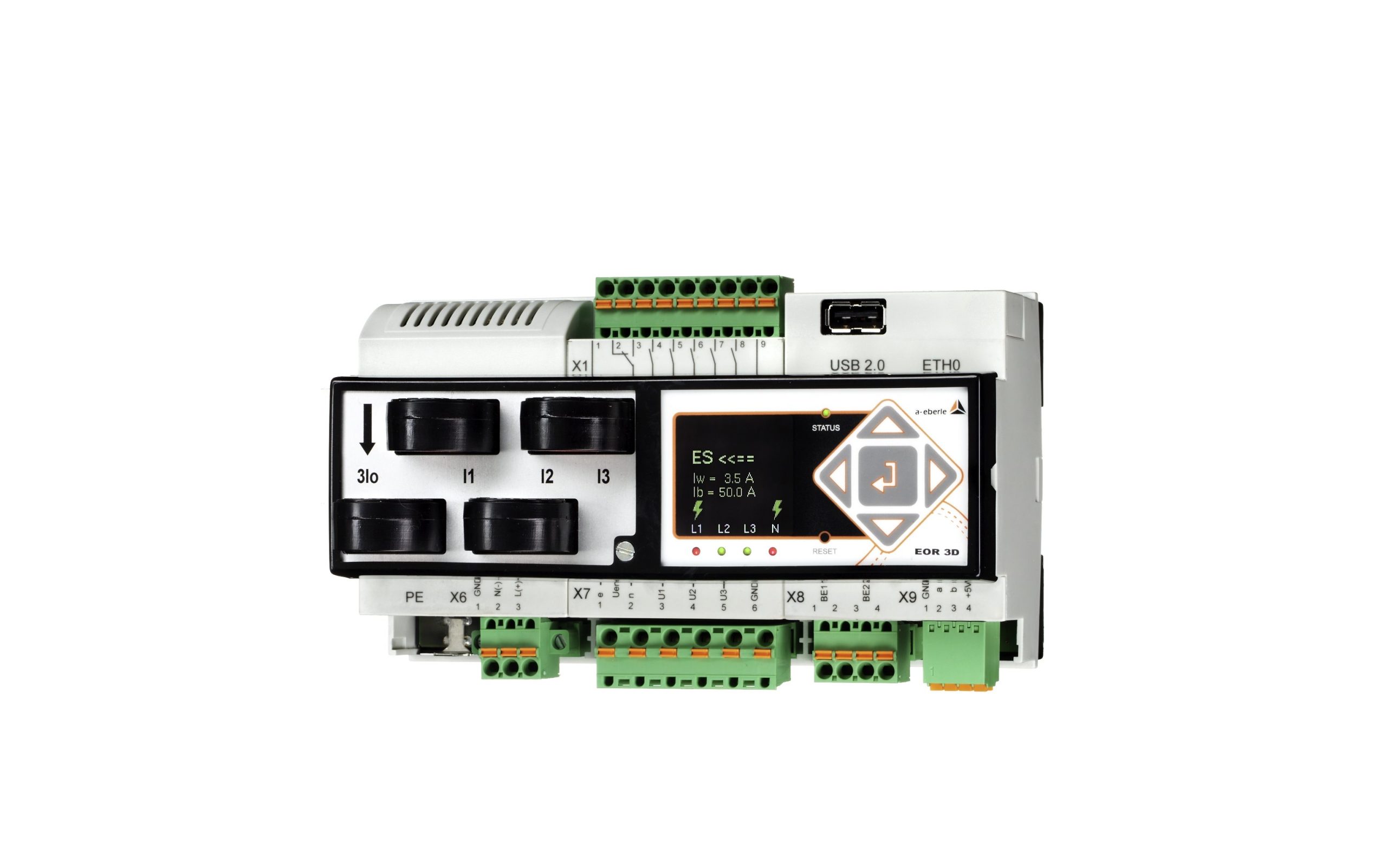
Thanks to the multi-frequency current injection’s compact form, it can fit into any existing control cabinet. During operation, up to eight different frequencies can be fed in directly via the auxiliary power winding of the suppression coil, i.e. without additional inductors, as required by other current injections. In addition, the MCI is able to both feed in power via the auxiliary power winding AND measure the zero-sequence voltage, without the feed negatively affecting the measurement. There is no need for zero-sequence voltage measurements to be decoupled from the e-coil.
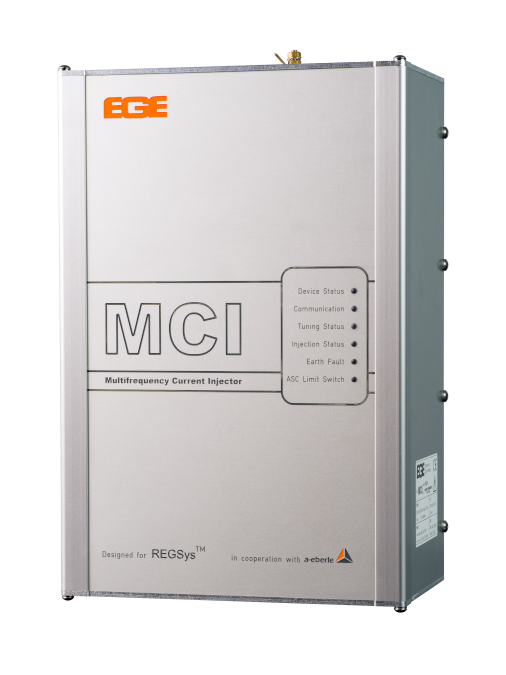

Can be deployed for 20 kV networks to 1300 A Ice
The multi-frequency current injection MCI can be used in 20 kV networks with average damping at up to 1300 A (capacitive earth current). The MCI can also be used in networks with lower or higher nominal voltages, whereby the maximum capacitive earth current will change in indirect proportion.
Includes automatic power reduction
The multi-frequency current injection MCI can be used in 20 kV networks with average damping and up to 1300 A (capacitive earth current). For very small networks, the current injection can lead to undesirably strong influences on the zero-sequence voltage, meaning in the worst-case scenario that the earth fault threshold may be crossed. To prevent this, the MCI monitors influences on the zero-sequence voltage and reduces them as needed automatically. The MCI can also be used in networks with lower or higher nominal voltages, whereby the maximum capacitive earth current will change in indirect proportion.

IO cabling to MCI also possible incl. emergency positioning
To simplify the cabling between the REG-DP(A), the MCI and suppression coil, the I/O signals (peak/trough commands, limit switch, potentiometer) can be wired directly to the MCI. In this case, only the communication needs to be cabled between REG-DP(A) and MCI (“Mode 1”). If the communications line between REG-DP(A) and MCI fails, the MCI can carry out emergency positioning.

Parametrisation control and connection via REG-DP(A)
By connecting the MCI unit to the REG-DP(A) regulator, the MCI can be parameterised, calibrated and controlled. Connection via all standard communications protocols is also possible. The REG-DP(A) regulator can be connected via REG-P, REG-PE or REG-PEDSV control units. The following protocols are available (further protocols on request):
- IEC 60870 -5 -101 / 103 / 104
- IEC 61850
- DNP 3.0 RTU / DNP 3.0 TCP
- MODBUS RTU / MODBUS TCP
- SPABUS
Do you have questions about
multi-frequency power feed?
Our specialists will be happy to help you!
Contact us
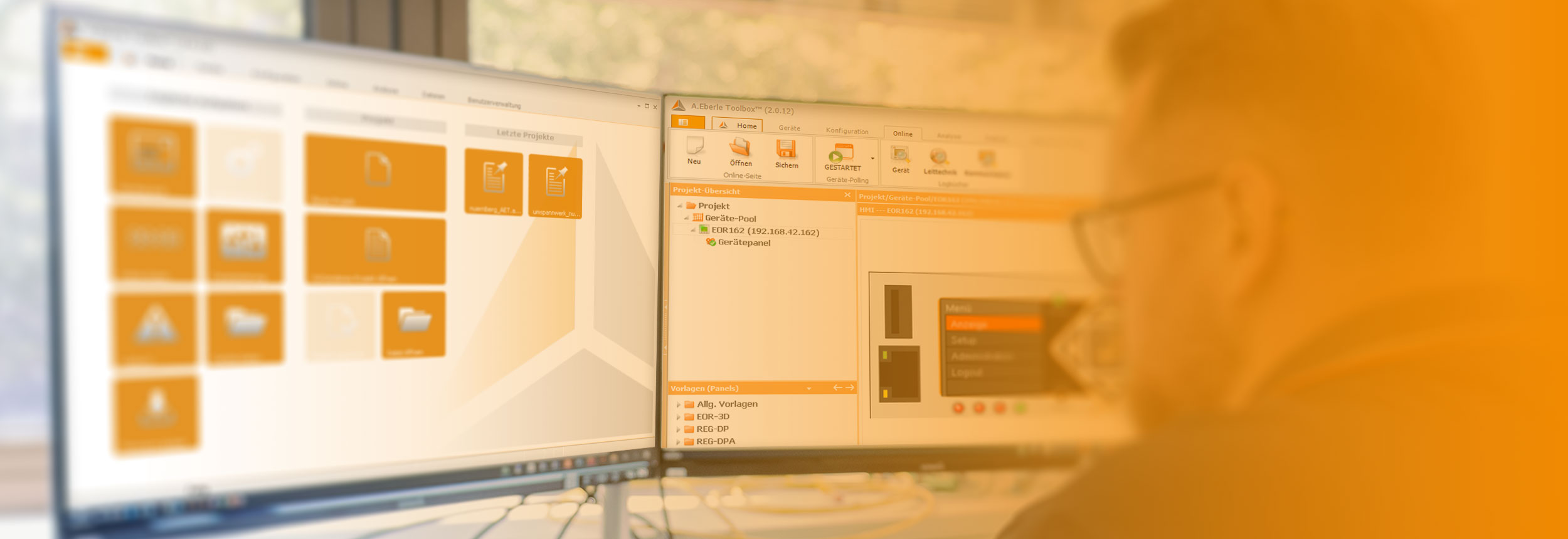
AE Toolbox
The perfect supplement to arc suppression devices: freely adjustable project planning and parameterisation software
The AEToolbox works on a project basis and impresses with its range of functions and the versatility that the program offers.