Table of Contents
What Is (Recording) Load Profile Measurement/Power Measurement and How Does It Work/Run?
What Is (Recording) Load Profile Measurement/Power Measurement?
Recording load profile measurement (RLM) and recording power measurement are essential methods in the energy supply sector for precisely recording the consumption of electricity and gas. These measurements are taken continuously and provide detailed insights into the energy consumption of commercial and industrial customers.
Are (Recording) Load Profile Measurement and (Recording) Power Measurement to Be Used as Synonyms or Are There Differences?
While RLM and recording power measurement are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences in their application. RLM focuses specifically on the consumption of electricity in quarter-hourly resolution and is mandatory for customers with an annual consumption of over 100,000 kWh or with high feed-in capacities (e.g. large industrial companies). Recording power metering, on the other hand, continuously records the consumption of electricity and gas and offers commercial and industrial customers detailed billing as well as the opportunity to reduce grid charges by optimising their load profile.

How Exactly Do (Recording) Load Profile Measurement and (Recording) Power Measurement Work?
Recording load profile measurement (RLM) is carried out using suitable measurement technology technology that records electricity consumption at least every quarter of an hour. These measured values provide commercial and industrial customers with a precise insight into their consumption and make it possible to reduce grid charges by optimising their load profile in a targeted manner. The data is either provided by the electricity supplier or can be sent directly to the consumer for an additional charge. Grid operators use the information from the RLM to prevent grid overloads and to optimise their grids. Large consumers (e.g. industrial companies) can collect their own measurement data in order to be able to track actual self-consumption and also make statements about standardised voltage and power quality. Provided that the measurement technology used can also measure power quality in addition to RLM.
Recording power measurement covers both electricity and gas consumption and has a similar function to RLM. In this case, the continuous measurements (not quarter-hourly) provide customers with accurate bills and allow them to better control their energy consumption. Grid operators use the data to avoid grid overloads, while energy suppliers can optimise their procurement and offer more favourable tariffs based on the load data collected.
Source for the definitions: Technical Minimum Requirements for Energy (TMA)
In summary, RLM measurement, also known as RLM current or RLM storm, and recording power measurement are important instruments for precisely recording and optimising energy consumption in industry and commerce.
Which Measuring Devices Are Needed for an RLM?
Functions of Measuring Devices for Load Profile Measurements
To carry out a load profile measurement, measuring devices must provide various functions in order to accurately record energy consumption. These include, among others:
- Recording power measurement (RLM): This is an essential feature, as RLM meters measure the average value of the power consumed at regular intervals.
- Continuous recording: The meters must be able to continuously record the power consumed and ideally transmit it at short intervals in order to create a precise load profile.
- Transmission to the distribution grid operator: The recorded data must be automatically transmitted to the distribution grid operator to enable accurate billing.
- Compliance with legal requirements: The metering periods are set by law, for example at 15 minutes for electricity. The metering devices must meet these requirements in order to fulfil the legal regulations.
Standards and regulations for measuring devices
Certain standards and regulations apply to measuring devices for load profile measurement and must be observed. The relevant standards and regulations include
DIN EN 50470-1
This standard specifies requirements for measuring devices for transformer measurement of electrical energy.
DIN EN 50470-3
This standard specifies the requirements for load profile meters, in particular with regard to electrical characteristics and communication interfaces.
ISO 9001
This is an internationally recognised standard for quality management systems, which ensures that the manufacture and operation of measuring devices meet the highest quality standards.
Load Profile Measurements With A. Eberle Devices
Load profile measurements can be carried out with A. Eberle Power Quality measuring devices. A. Eberle offers a range of measuring devices that fulfil the requirements for precise load profile measurement.
A. Eberle Devices for Load Profile Measurements
Which Devices Can Be Used to Carry out Load Profile Measurements?
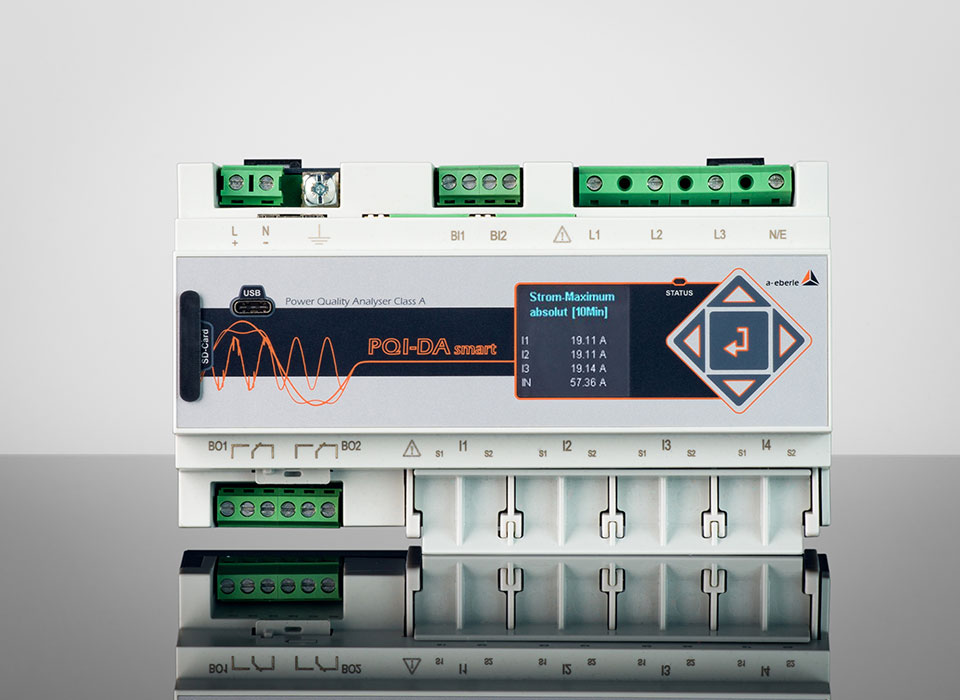
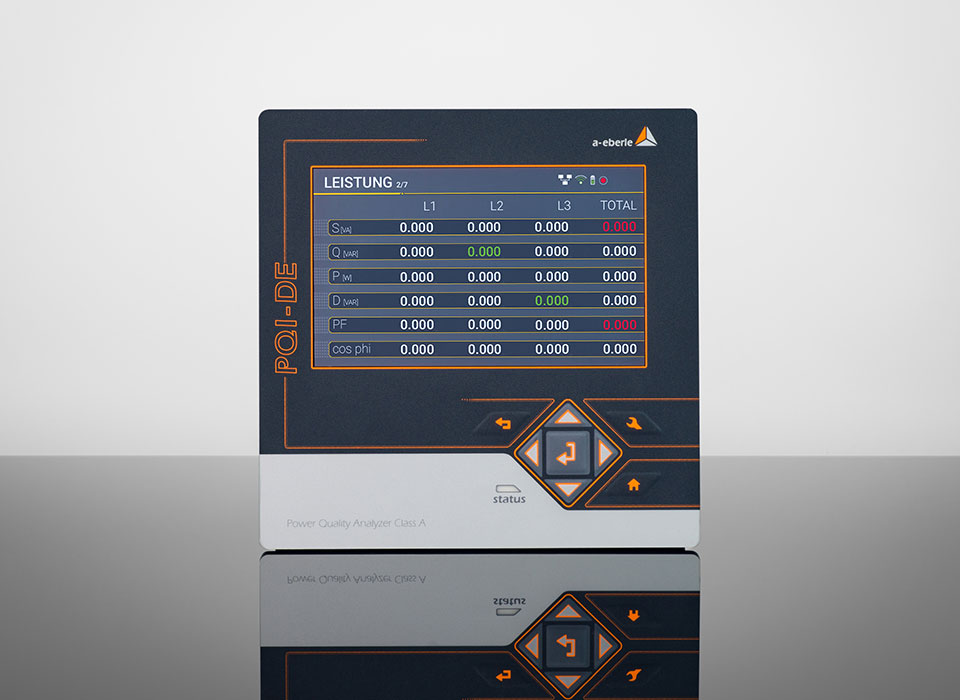
High-precision load profile measurement/load profile analysis is possible with any model of our permanently installed power quality analysers, as well as with any of our mobile power quality measuring devices. From the permanently installed »PQI-DE« measuring device, which permanently monitors the entire feed-in and documents faults retrospectively and traceably, to our mobile devices, such as the »PQ-Box 150« , which is used for temporary measurement tasks in the depth of the grid (e.g. connection of a single machine). With the soon-to-be-released »PQ Box ONE« single-phase power quality analyser for sockets, single-phase loads can also be analysed very easily in order to record energy consumption in a targeted manner.
Special Features of A. Eberle Appliances
What Special Features/Advantages Do These A. Eberle Devices Offer for Load Profile Measurements Compared to Other Measuring Devices?
All power quality measuring devices (fixed and mobile) from A. Eberle are class A measuring devices in accordance with IEC 61000-4-30, enabling highly accurate power quality measurements in addition to load profile analysis and energy recording. The devices are easy to use and have a very user-friendly and intuitive »WinPQ mobil« analysis software. Our mobile PQ boxes can initially be purchased in a simple version and further customised/upgraded depending on your application requirements. If, for example, you require additional functions at a later date to record certain/specific faults in the grid, you can easily upgrade your device using a licence code. It is not necessary to purchase a new device.
Sample Measurements With Our High End Portable Power Analysers
Some Impressions From The »WinPQ mobil« Analysis Software – 15-Minute Load Profile Measurement, Interval Energy, Energy Consumption per Phase, Total Power & CO2 Consumption
Click on the respective images to enlarge the view:





Our Portable & Fixed Installed PQ Grid Analysers
Load Profile Analyser, Energy Logger & Grid Analyser With One Device
What Is Evaluated When Analysing the Load Profile Measurement/Analysing the Load Profile?
Analysis & Evaluation of the Load Profile Measurement
Aspects Analysed
When analysing load profile measurement, also known as load profile analysis, various aspects of electricity use are examined in order to gain insights into energy consumption.
Analysed Parameters and Key Figures
The Load Profile Analysis Collects and Evaluates a Large Number of Parameters and Key Figures, Including:
- Load profiles: The distribution of energy consumption over a certain period of time.
- Peak loads: The maximum values of energy consumption within a specific time interval.
- Base loads: The minimum continuous load on the electricity grid.
- Load shifts: Changes in consumption behaviour that can occur at different times, e.g. during peak load periods or depending on production cycles.
- Power factors: The ratio of actual power to apparent power, which provides information on the efficiency of electricity utilisation.
- Deviations from the average: Differences in consumption behaviour compared to an average load profile.
Results and Recommendations for Action
The Results of the Load Profile Analysis Can Provide Various Insights and Enable Appropriate Recommendations for Action:
- Identification of potential savings: By analysing load profiles, inefficient consumption patterns can be identified that offer opportunities to reduce energy consumption.
- Optimisation of the load profile: Targeted measures, such as load shifting or load management, can be used to optimise the load profile in order to reduce peak loads and improve energy efficiency.
- Investment planning: The analysis can provide information on whether investments in energy-saving measures or the installation of additional capacity are required to cover current and future energy requirements.
- Investment planning: The analysis can provide information on whether investments in energy-saving measures or the installation of additional capacity are required to cover current and future energy requirements.
When and Where Is Load Profile Measurement Necessary/Useful?
For PV System Operators
When Is Load Profile Measurement Necessary?
For operators of photovoltaic systems (PV systems), load profile measurement is required in various scenarios:
- Mandatory for certain systems: According to VDE regulations, PV systems above a certain size must be controllable by the grid operator. This requires continuous monitoring of the actual output or feed-in, which can only be guaranteed via an RLM meter.
- Systems from 100 kWp must be controllable by the grid operator in order to be able to assess the impact on the electricity grid, which is only possible via an RLM meter.
- Direct marketing: PV systems that are integrated into direct marketing must install an RLM meter, regardless of their installed capacity.

- System size: PV systems without direct marketing and with an output of 100-500 kW must also have an RLM meter to enable precise measurement of the feed-in.
The Purpose and Benefits of Regular Load Profile Measurements
Carrying out Regular Load Profile Measurements Offers PV System Operators Various Advantages:
Efficient Planning
Regular load profile measurements allow PV system operators to better plan their feed-in and recognise potential savings. This leads to greater planning reliability and cost control.
Optimisation of the Feed-In
Knowledge of the load profile enables PV system operators to optimise their feed-in and avoid bottlenecks in the grid. This can contribute to improved grid stability.
Fulfilment of Legal Requirements
By installing an RLM meter, PV system operators fulfil the legal requirements and regulations, which leads to smooth integration of their system into the electricity grid.
For Companies
When Is Load Profile Measurement Necessary?
For Companies, Load Profile Measurement Is Required in Various Situations:
- Legal requirements: According to the Electricity Grid Access Ordinance (StromNZV) and the Gas Grid Access Ordinance (GasNZV), companies are obliged to carry out recording power metering from a certain level of consumption.
- In Germany, the Electricity Grid Access Ordinance (StromNZV) requires companies with an annual consumption of 100,000 kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity or more to carry out recording power metering.
- For gas consumers, the Gas Grid Access Ordinance (GasNZV) specifies two criteria: an annual consumption of over 1.5 million kWh and an output of 500 kW.

- Optimisation of energy costs: Companies with a high consumption of commercial electricity or gas can reduce their grid charges and thus their energy costs by shifting loads and optimising their load profile.
- Transparency and cost control: The regular recording of load data provides companies with transparency about their energy consumption and enables a more accurate cost calculation. This leads to improved cost control and planning security.
The Purpose and Benefits of Regular Load Profile Measurements
Regularly Carrying out Load Profile Measurements Brings Companies Various Advantages:
Cost Optimisation
By knowing the load profile, companies can lower their energy costs by reducing their grid charges and utilising potential savings.
Efficient Planning
The regular recording of load data enables companies to better plan their energy consumption and identify potential savings.
Rapid Response to Consumption Deviations
By monitoring their load profile, companies can quickly identify consumption deviations and react accordingly in order to avoid production downtimes and optimise their operating processes.
What Is a Standard Load Profile/SLP and How Does It Work/Run?
Standard Load Profile (SLP): Definition and Meaning
What Is a Standard Load Profile/SLP?
A standard load profile (SLP) is a standardised representation of the expected electricity consumption over a certain period of time for different consumer groups. It is used to track time and temperature-dependent fluctuations in electricity consumption and to ensure that sufficient electricity is available to consumers at all times.
The Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy defines the standard load profile as follows:
“Standard load profiles are typified consumption profiles of customers that are determined by the grid operators based on the actual consumption of customers with comparable characteristics.” (Source: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy)
When Is It Necessary to Measure the SLP?
The measurement of the SLP is particularly necessary if a standardised recording of the electricity consumption for a specific consumer group is required. This may be the case in the following situations:
- Billing: Standard load profiles are often used to estimate consumption for the billing of electricity consumption by households, commercial enterprises or other consumer groups.
- Grid planning: When planning and dimensioning electricity grids, SLPs are used to forecast the expected electricity demand of the various consumer groups and to adjust the grid capacities accordingly.
Sense and Benefits of Regular Measurements of the SLP
Efficient Planning and Security of Supply
Regular Measurement of the SLP Offers Various Advantages:
Planning Reliability
By regularly updating and adjusting the SLPs, grid operators and energy suppliers can better forecast their customers’ electricity requirements and take appropriate measures to ensure a continuous supply.
Efficient Use of Resources
Precise recording of electricity consumption according to standard load profiles enables grid operators to utilise their resources more efficiently and avoid bottlenecks in the electricity grid.
Customer-Orientation
The use of SLPs enables energy suppliers to offer their customers customised tariffs and services that correspond to their individual consumption profiles.
Risks and Disadvantages Without Regular SLP Measurements
Without Regular Measurements and Updates of the SLPs, Grid Operators and Energy Suppliers Run Various Risks:
Uncertainty in Supply Planning
Without up-to-date data on the consumption behaviour of customers according to standard load profiles, there is a risk of misjudgements in supply planning, which can lead to bottlenecks or overcapacity in the electricity grid.
Inefficient Use of Resources
Without precise consumption forecasts according to SLPs, grid operators can utilise their resources inefficiently, which can lead to higher costs and lower security of supply.
Limited Customer Orientation
Without up-to-date data on consumption behaviour according to SLPs, energy suppliers cannot offer their customers customised tariffs and services, which can lead to lower customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Which Measuring Devices Are Needed to Measure the Standard Load Profile/SLP?
Suitable Measuring Devices for Measuring the Standard Load Profile (SLP)
Functions of SLP Meters
To measure the standard load profile (SLP) precisely, measuring devices must have certain functions:
Manual Reading and Display
SLP meters must be able to read the actual electricity and/or gas consumption manually and show it on a display.
Estimated Consumption
With SLP meters, the monthly discounts are based on estimated values based on the standard load profile and statistical-mathematical procedures. This simplifies the billing and metering processes.
Adjustment of the Discounts
In the event of deviations between the estimated values and the actual consumption, the discounts are adjusted after the meter reading and annual invoice.
Standards and Regulations
Certain standards and regulations apply to SLP meters to ensure their functionality and accuracy:
DIN EN 62053
This standard specifies the requirements for electrical energy meters, including meters for the standard load profile.
DIN EN 1359
This standard applies to gas meters and specifies requirements for the accuracy and performance of gas meters.
Compatibility With A. Eberle Devices
The measurement of the standard load profile is possible with all power quality measuring devices (fixed and mobile) from A. Eberle. In addition to measuring the SLP/load profile analysis and energy recording, the devices offer the option of high-precision power quality measurements (IEC 61000-4-30, Class A). The devices are easy to use and have very user-friendly and intuitive analysis software.
Standards and Regulations for SLP Meters
Requirements for SLP Meters According to DIN en 62053
DIN EN 62053 specifies the requirements for electrical energy meters, including those used for the standard load profile. This standard ensures that SLP meters have the required accuracy and performance to record actual consumption according to the standard load profile.
Requirements for Gas Meters According to DIN en 1359
Gas meters are subject to the requirements of DIN EN 1359, which specifies accuracy and performance requirements for gas meters. This standard ensures that gas meters used to measure the standard load profile meet the required standards and provide reliable measurement results.
Differences Between SLP and RLM
The differences between RLM (Recording Load Metering) and SLP (Standard Load Profile) can be summarised as follows:
Target Groups
RLM Customers
Large consumers such as large companies, industrial operations and large solar parks.
SLP Customers
Small consumers such as private households and small businesses.
Measuring Method
RLM (Recording Power Measurement)
Measures actual consumption at short intervals (15 minutes for electricity), transmits the data continuously and enables accurate billing based on actual consumption.
SLP (Standard Load Profile)
Based on standardised consumption profiles and uses statistical methods to estimate consumption. Readings are usually taken once a year by the customer.
RLM and SLP Measurement With A. Eberle Messtechnik: Both methods, the recording power measurement as well as the measurement of the standard load profile, are easily and reliably possible with all models of our mobile and permanently installed grid analysers. In addition, our Class A measuring devices (IEC 61000-4-30) also offer you the option of energy recording, fault recording and high-quality power quality analysis, also as part of a complete grid analysis.
Billing
RLM
Monthly billing based on precise consumption data.
SLP
Billing is based on estimated values and is adjusted once a year.
Concrete Differences for the Customer
For RLM Customers
RLM-Kunden profitieren von einer präzisen und kontinuierlichen Erfassung ihres Energieverbrauchs. Dies ermöglicht:
- More accurate billing: Monthly billing is based on actual consumption data, which leads to a fairer and more accurate distribution of costs.
- Recognising potential savings: By recording consumption in detail, peak loads can be identified and reduced through targeted measures, resulting in cost savings.
- Grid stability: Continuous data collection supports grid operators in ensuring grid stability and efficient planning of energy requirements.
For SLP customers
SLP customers experience a less complex and more cost-effective measurement process. However, there are some disadvantages:
- Inaccurate billing: monthly instalments are based on estimated values and are only adjusted accurately after the annual meter reading, which can lead to additional payments or refunds.
- Less transparency: The lack of continuous data collection means that SLP customers have less insight into their actual energy consumption, which makes it more difficult to recognise potential savings.
- Less flexibility: Billing according to SLP profiles offers fewer opportunities to optimise and adapt consumption behaviour to specific tariff features.
Official Definitions
The Official Definition of the Standard Load Profile (SLP) According to the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy Is as Follows:
“Standard load profiles are typified consumption profiles of customers that are determined by the grid operators based on the actual consumption of customers with comparable characteristics.” (Source: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy)
Recording Performance Measurement (RLM) Is Often Defined as Follows:
“Recording power metering (RLM) is a metering method that records actual energy consumption at regular intervals and transmits it continuously to the grid operator.” (Source: E.ON)