General Info
For the parallel connection of power sources, the principle of superposition applies, when all resources have a linear behaviour. This behaviour is the case with current transformers within the allowable load range and below a few thousand Hertz. It should be noted that in principle and device technically only simultaneous instantaneous values are added, not effective values!
Through the common load resistor RL of parallel current transformers a current flows that corresponds to the arithmetic sum of the instantaneous values of all the currents. It is assumed that the current transformers provide superimposed currents and the frequency limits (highest order of the harmonics) are not exceeded.
The arithmetic sum of the instantaneous values is not only dependent on the amount, but also the sign of the individual currents, so that for the summation the polarity of the current sources must be considered. With alternating currents of the same direction of energy flow, the polarity is related to the secondary terminals S1 (k) and S2 (l) of the current transformer.
Waveform of the total current
When summing equal frequency sinusoidal currents, the curve of iS has the form of a sinusoidal curve, with currents of unequal frequency the waveform of the total current i is no longer sinusoidal.
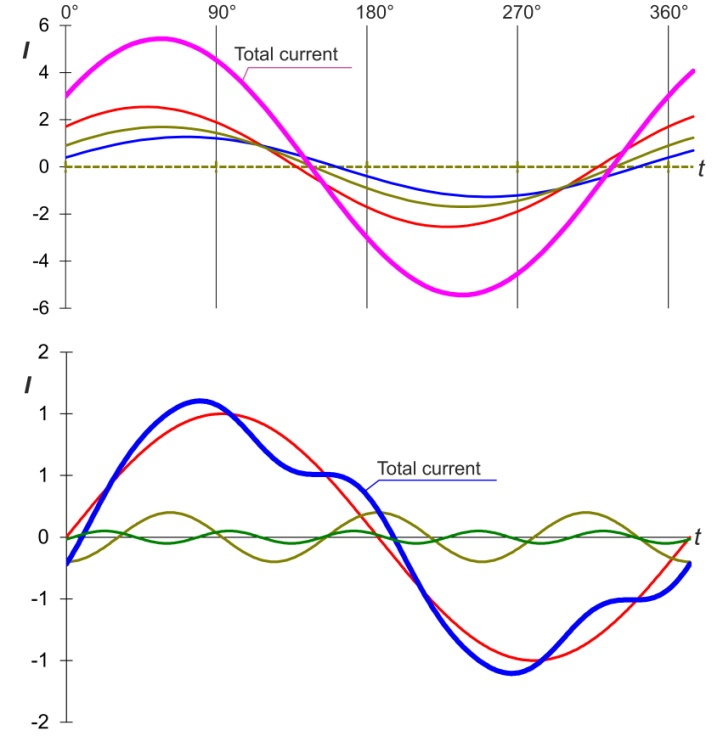
a) with the same frequency
b) with different frequencies
Sum of the instantaneous values
For the three-phase three-wire network with the same frequency sinusoidal currents, the simultaneous instantaneous values are ideally zero.
Effective value of the total current
For the calculation of the effective value of the total current from the momentary values of current with an arbitrary frequency/waveform the following applies:
I_{\sum} = \sqrt{\frac{1}{T}\int_{T}^{0}(i_{0} +i_{1}+i_{2}+...+i_{n})^{2} dt }i_{0} +i_{1}+i_{2}+...+i_{n}Arithmetic sum of the simultaneous current components
For the calculation only of the effective values of currents with different frequencies (e.g. equal value/ fundamental with harmonics) the following also applies:
I_{\sum} = \sqrt{I^{2}_{0} +I^{2}_{1}...+I^{2}_{n} }I0 = Effective value of the direct current
I1 = Effective value of the fundamental
In = Effective value of the highest harmonic