Three simultaneous processes
When there is an earth fault in a conductor, at the start of the earth fault three events occur at the same time.
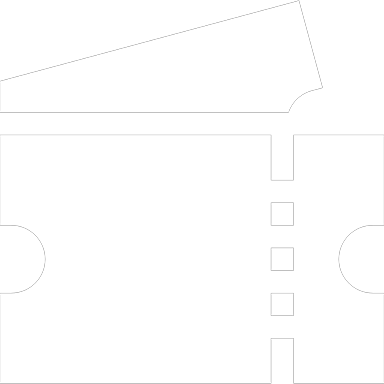
- The voltage U1E (phase-earth) of the conductor affected by the earth fault collapses, with a saturated earth fault U1E goes to zero
- the zero sequence voltage UNE rises abruptly from the operating value (a few volts) to a higher value;
with a saturated earth fault - the capacitance CLE (phase-earth) of the faulty conductor is discharged while the charge state of the capacitances CLE of the two fault-free conductors is also abruptly changed (recharged) (up to ULL) by the simultaneously varying voltage U1E
Zero sequence voltage
The zero sequence voltage UNE occurs regardless of the location of the earth fault in the entire electrically connected network in nearly the same way and has the same waveform and frequency as the line voltage. The zero sequence voltage UNE is present as long as the earth fault persists.
Discharge of CLE of the earthed conductor
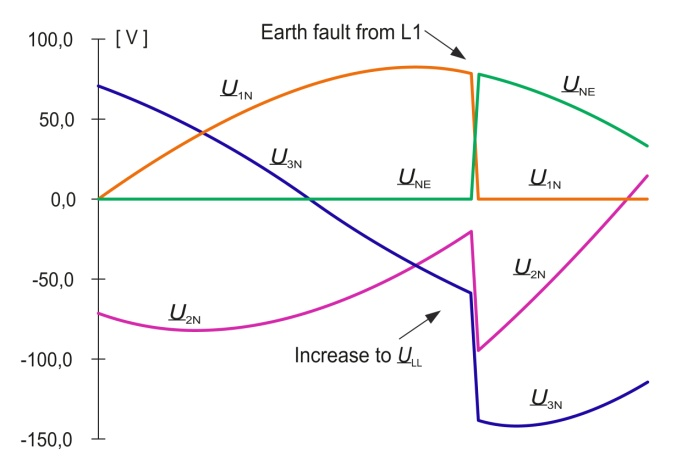
When there is an earth fault in a conductor, the capacitance CLE of all the lines of the electrically connected network discharge across the earth fault to earth. This process occurs only once immediately after the start of the earth fault and is completed in a short time.
The timing of this discharge current is dependent on the data of the conductor. The ratio of the ohmic resistance to the inductance of the conductor determines the properties of the resonant circuit consisting of these elements. If the inductance is relatively small, the discharge current is an aperiodic, steadily decaying DC; with larger inductance values it is a periodic decaying alternating current.
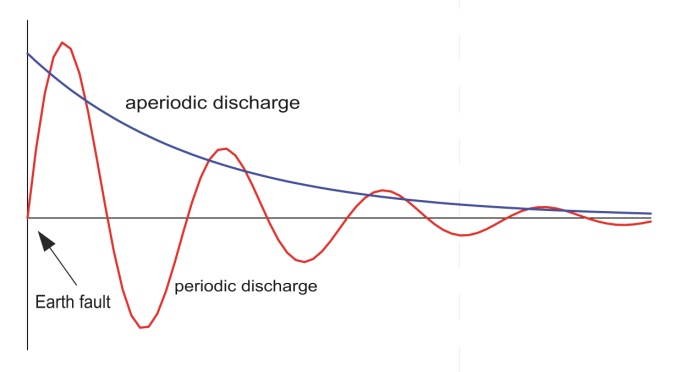
The amplitude of this current surge is dependent on the time of occurrence of the earth fault. If this coincides with the maximum of the half-wave of ULN, the initial amplitude of the current surge also reaches the maximum and it goes to zero if the fault occurs during the zero crossover.